Getting A Handle On VPC Pricing: What You Need To Know
Figuring out how much your cloud setup costs can feel like a big puzzle, especially when it comes to things like virtual private clouds, often called VPCs. These private network areas in the cloud are super useful, giving you a place to put your digital resources where you have a lot of say over how things work. But, you know, knowing the price tag for using these services, like Amazon VPC, is a pretty important step for anyone trying to keep their spending in check. So, we're going to talk about what makes up those bills, helping you get a clearer picture of what you might pay.
A virtual private cloud, or VPC, is a special part of a big public cloud, like AWS or Google Cloud, where you get to set up your own isolated network. It is a bit like having your own private office space inside a very large building. This separation gives you a lot of privacy and also a good amount of security for your digital stuff. Companies use VPCs to run their applications and store their information, keeping it separate from what others are doing in the same cloud system, which is a pretty good thing to have.
When you put your resources into a VPC, you usually get an IP address for them, which helps them connect to other things. This setup lets you control your network environment quite a bit. But, you know, getting that control comes with its own set of charges. These charges can add up, and knowing what affects them, like data moving around or certain features you turn on, is really helpful for keeping your cloud bills from getting too big. So, we will look at those different parts of the price tag.
Table of Contents
- What Is a VPC and Why It Matters
- The Main Things That Cost Money in VPC Pricing
- How to Keep Your VPC Costs Down
- VPC Pricing Across Different Cloud Providers
- Frequently Asked Questions About VPC Costs
- Final Thoughts on Managing Your VPC Spending
What Is a VPC and Why It Matters
A virtual private cloud, often called a VPC, is a way to create a section of a public cloud that feels very much like your own private network. It allows people to logically separate their resources into different network spaces, which is pretty useful. You get to decide how things connect, what security rules are in place, and where your data goes. This kind of setup gives you, the person in charge, a lot of say over your digital environment, which is a big deal for keeping things safe and running smoothly.
The idea behind a VPC is to give you a private, isolated part of a big cloud system where you can launch and run your applications and services. It is a bit like having your own dedicated server room, but it is all happening in the cloud, which is kind of neat. This isolation is a key reason why many businesses use VPCs. It helps them meet security rules and keep their sensitive information away from other users on the public cloud, which, you know, gives a lot of peace of mind.
When you set up a VPC, nearly all the things you put inside it, like your virtual servers, get their own IP address for connecting. This means they can talk to each other and to the outside world based on the rules you set up. Whether you are using a VPC network or an older type of network, the way you are charged for some things, like traffic between different zones in the same area, often stays the same. This can make planning your network a little easier, in some respects.
The Main Things That Cost Money in VPC Pricing
When you look at VPC pricing, there are a few big areas where charges typically show up. These are the parts that can make your monthly bill go up or down quite a bit, so understanding them is pretty important. We are going to go through the most common ones, like how much data moves around, and what happens when you use certain network tools. So, knowing these points helps you manage your money better, which is actually a pretty good idea.
Data Transfer Charges
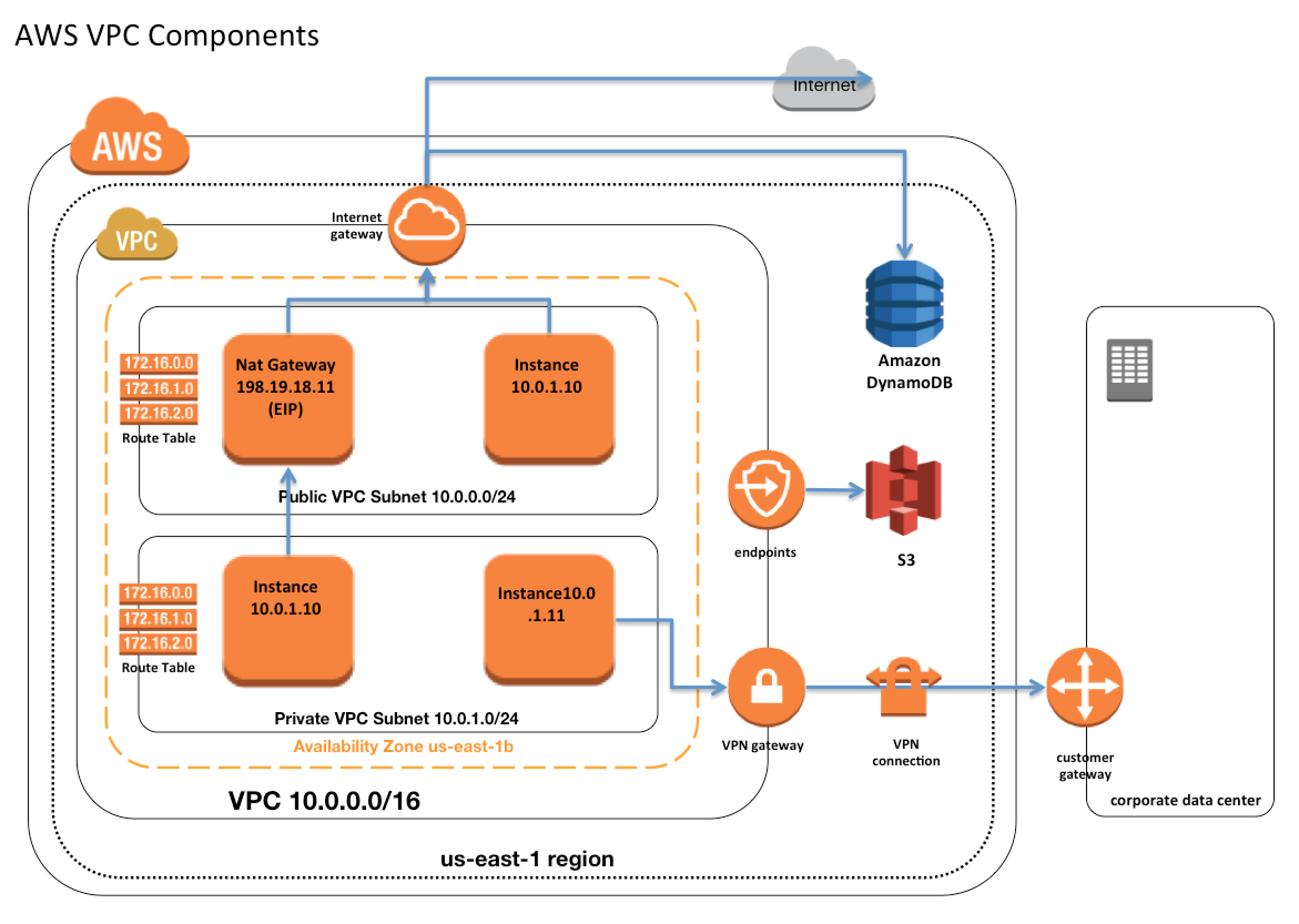
One of the biggest parts of VPC costs often comes from moving data around. This includes information going into your VPC, out of your VPC, and sometimes even between different parts within your VPC. For example, if your cloud resources send or receive a lot of information, those data transfer charges can really add up. It is a bit like paying for every mile your car drives, you know, the more miles, the more gas you use, and the more it costs.
The price for traffic between different zones in the same region, for instance, is usually the same. This holds true whether your two virtual machines are in the same network segment, different segments, or even different network setups. This consistency is somewhat helpful for predicting costs for data moving within a particular cloud area. But still, the total amount of data moved is what really drives this part of the bill, so you really need to watch that.
It is important to remember that these data transfer fees are not just for what leaves the cloud. They can also apply to data moving between different availability zones, or even within the same region but across different services. So, if you have applications that talk to each other a lot and they are spread out, you might see these charges increase. Keeping an eye on how your applications communicate is a key step to keeping these costs in check, as a matter of fact.
NAT Gateway Costs
NAT Gateways are another area where VPC pricing can get a bit interesting. These gateways help your private resources in the VPC connect to the internet without having a public IP address themselves. This is a common setup for security reasons. However, there are charges for every gigabyte of data that goes through the NAT Gateway, no matter what kind of traffic it is. This means that if your applications are constantly reaching out to the internet, these data processing charges can become pretty significant.
For instance, if you have a lot of virtual machines or containers making updates, downloading packages, or connecting to external services, all that data passes through the NAT Gateway. Each gigabyte processed through it adds to your bill. This is a very common place where people find unexpected costs because they might not realize just how much data their background processes are handling. So, it is a good idea to look at how much information your applications are sending and receiving through this path.
There are definitely ways to help reduce these data transfer charges for your NAT Gateway, which we will talk about a little later. But for now, just know that this component is a notable part of the VPC pricing picture. It is one of those things that, if you are not careful, can quietly make your cloud spending go up more than you might expect. So, keeping an eye on it is a pretty smart move, you know.
Traffic Mirroring and ENI Charges
Some advanced features, like VPC traffic mirroring, also come with their own price tags. If you decide to turn on traffic mirroring for an Elastic Network Interface (ENI) on your Amazon EC2 instances, the owner of that ENI will get charged by the hour for each ENI that has this feature active. This is a specialized service that lets you copy network traffic for things like security monitoring or troubleshooting. So, while it is useful, it is not free.
This hourly charge for traffic mirroring applies whether the traffic is going into or out of your instance. It is another example of how specific features within a VPC can add to your overall bill. You might not use traffic mirroring all the time, but when you do, it is important to know that it comes with a continuous charge. This is a bit like paying for a special tool only when you are actively using it, which is fair enough, but you still need to account for it.
It is worth noting that these charges can sometimes vary by region, too. For example, in certain regions like China (Ningxia, Beijing), the pricing for VPC traffic mirroring might have its own specific rates. So, if you are running your cloud setup in different parts of the world, it is always a good idea to check the pricing details for each specific area to avoid any surprises. This is a pretty important detail to keep in mind, honestly.
IP Address Costs
When you set up resources in your VPC, they often get an IP address for connecting. While many IP addresses are free when they are connected to a running instance, you can sometimes incur charges for IP addresses that are not being used. For example, if you allocate a public IP address but do not attach it to a running virtual machine, you might get charged a small hourly fee for it. This is basically to encourage people to release IP addresses they are not actively using, helping the cloud provider manage their available addresses.
This cost is usually pretty small on its own, but if you have a lot of unused IP addresses lying around, they can add up over time. It is one of those tiny things that can sneak onto your bill if you are not paying attention. So, it is a good practice to regularly check your VPC setup and make sure you are not holding onto IP addresses that are just sitting there doing nothing. You know, it is a bit like having an empty parking spot you are still paying for.
Some cloud services might also charge for certain types of IP addresses, like Elastic IP addresses, even when they are associated with a running instance, if they are not actively transferring data. The rules can be a little different depending on the cloud provider and the exact service. So, it is always a good idea to look at the specific pricing pages for your chosen cloud platform to understand all the details about IP address charges. This is definitely something to look into, actually.
How to Keep Your VPC Costs Down
Once you get a better idea of what makes up your VPC bill, the next logical step is to figure out how to spend less. There are a few good strategies you can use to reduce your cloud spending, especially when it comes to networking charges. These ideas often involve making smarter choices about how your applications send and receive information, and how you use certain network tools. So, let us talk about some practical ways to save some money, which is pretty useful for anyone.
Watching Your Data Movement
One of the best ways to cut down on VPC costs is to be smart about data transfer. Data processing charges, as we mentioned, can be a big part of the bill. For example, if your AWS resources send or receive a lot of information, those costs can really add up. Try to keep data within the same region or, even better, within the same availability zone whenever you can. Moving data across regions or out to the internet usually costs more, so that is something to think about.
You might also look at compressing your data before it moves, which can reduce the total amount of gigabytes transferred. This is a bit like putting more clothes in a smaller suitcase, you know, making it more efficient. Also, if you have services that talk to each other a lot, try to place them closer together in your network setup. This can sometimes mean putting them in the same subnet or availability zone, which can help lower those inter-zone transfer fees, in a way.
Another thing to consider is how often your applications are pulling data. If something is constantly downloading large files, you might look for ways to cache that data closer to where it is needed or reduce the frequency of those downloads. Every little bit of data you save from moving across networks can add up to real savings over time. So, paying attention to your data flow is a very practical step, honestly.
Making NAT Gateways More Efficient
Since data processing charges apply for each gigabyte processed through the NAT Gateway, regardless of the traffic's type, making your NAT Gateway usage more efficient is a good way to save. One common strategy is to use private endpoints or VPC endpoints for connecting to other cloud services, like S3 or DynamoDB, when possible. This keeps the traffic within the cloud's private network, bypassing the NAT Gateway entirely, which can save you a good amount of money on those data processing fees.
Another idea is to consolidate your NAT Gateways if you have many of them. Sometimes, people set up a NAT Gateway in every single subnet, but you might only need one per availability zone. This can reduce the number of gateways you are paying for hourly. Also, consider if all your instances truly need internet access through a NAT Gateway. Some instances might only need to talk to other private resources, and for those, you might not need to route their traffic through a NAT Gateway at all, which is pretty helpful.
You can also use a proxy server or a Squid cache behind your NAT Gateway for instances that need to access the internet for things like software updates. This can help reduce repetitive downloads and thus lower the amount of data going through the NAT Gateway. So, thinking about how your instances use the internet and optimizing that path can really help cut down on those specific charges, you know, which is a pretty good outcome.
Choosing the Right Services
Sometimes, the choice of cloud services themselves can influence your VPC costs. For instance, if you are using a managed database service, the way it connects to your application instances within the VPC can affect data transfer. Some services offer private connectivity options that avoid public internet routes and associated data transfer charges. This is a bit like taking a shortcut that does not have a toll booth, which is quite nice.
Also, when you are setting up new applications, think about their network needs from the start. Can certain parts of your application be placed in the same availability zone to reduce inter-zone traffic? Are there serverless options, like AWS Lambda, that might handle some tasks without needing a dedicated instance in your VPC, potentially reducing network overhead? These kinds of choices can have a big impact on your overall bill, which is something to consider early on.
For example, if you are storing a lot of data, think about where that data lives and how often it needs to be accessed. Storing data in a region far from where your main applications are running will likely increase data transfer costs when that data is needed. So, trying to keep your data and compute resources geographically close within the cloud can be a very effective cost-saving measure, you know, it is a simple idea but it works.
Using Tools to Help You Save
There are also tools and services that can help you get a better handle on your cloud spending, including your VPC costs. Some companies, like CloudZero, help you discover key cost factors of Amazon VPC and learn how to optimize cloud spending for better control and efficiency. These tools often give you a clearer picture of where your money is going, showing you exactly which parts of your VPC are costing the most. This kind of insight is pretty valuable.
These specialized platforms can track your data transfer, NAT Gateway usage, and other network-related expenses in real time. They can also point out areas where you might be able to save money, like identifying unused IP addresses or inefficient data flows. It is a bit like having a financial advisor for your cloud bill, helping you make smarter spending decisions. So, using such tools can really make a difference, as a matter of fact.
Beyond third-party tools, cloud providers themselves offer cost management dashboards and billing reports. You can often set up alerts for when your spending reaches a certain level, which can help you catch unexpected increases quickly. Regularly checking these reports and using the insights they provide is a very good habit to get into. Understanding Google VPC pricing, for instance, is a key step toward optimizing your cloud costs, and using the right tools and strategies can really help you out.
VPC Pricing Across Different Cloud Providers
It is worth noting that while the core concepts of VPC pricing are similar, the specific details can vary between different cloud providers. Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a well-known service, but other providers like DigitalOcean and Google Cloud also offer their own versions of a virtual private cloud. For example, a virtual private cloud is a private network interface for collections of DigitalOcean resources, and their pricing structure might have its own unique points. This is something to keep in mind when comparing options.
For instance, Google VPC pricing might have different rates for data transfer or different ways of charging for certain network services compared to AWS. Similarly, other providers might bundle certain features or charge for them separately. The general principles of data movement, IP addresses, and specialized network features usually apply, but the exact numbers and how they are applied can change. So, if you are thinking about using a different cloud provider, you should always check their specific pricing pages.
The good news is that the core strategies for optimizing costs, like being smart about data transfer and efficiently using network services, tend to work across most cloud platforms. Whether you are looking at AWS, Google Cloud, or DigitalOcean, the goal is always to reduce unnecessary data movement and only pay for the network resources you truly need. So, while the numbers might be different, the approach to saving money is often quite similar, which is pretty convenient.
Frequently Asked Questions About VPC Costs
How does VPC pricing work in general?
VPC pricing usually depends on a few main things, like how much data moves into and out of your private network, and also between different parts of it. You might also pay for certain network features you turn on, such as NAT Gateways or traffic mirroring. It is often a pay-as-you-go model, meaning you only get charged for what you actually use, which is a common approach in cloud services, you know.
What are the main things that make my VPC bill go up?
The biggest cost drivers for VPCs are typically data transfer charges, especially for data moving out to the internet or between different regions. NAT Gateway data processing fees can also add up if you have a lot of traffic going through them. Sometimes, even unused IP addresses can contribute to your bill, so those are things to watch for, as a matter of fact.
What are some ways to lower my VPC spending?
To cut down on VPC costs, you can try to keep data movement within the same region or availability zone as much as possible. Using private endpoints for cloud services instead of routing through NAT Gateways can also save money. Regularly checking for and releasing any unused IP addresses is another simple way to reduce your bill, which is pretty helpful for keeping costs in check.
Final Thoughts on Managing Your VPC Spending
Getting a good handle on your **vpc pricing** is a pretty important part of managing your cloud budget effectively. It is not just about the big ticket items, but also about understanding the smaller, often overlooked charges that can add up. Things like data transfer fees, especially those tied to NAT Gateways, can really impact your overall spending. So, paying close attention to these details can make a big difference in your monthly bill, which is pretty good news for anyone trying to save money.
Remember, whether you are using Amazon VPC, Google VPC, or another provider's service, the principles of cost optimization remain fairly consistent. The price on traffic between zones in the same region is the same if the two instances are in the same subnet, different subnets, or different networks, and this kind of consistency can help with planning. By regularly checking your usage, making smart choices about where your data moves, and using tools to track your spending, you can keep your cloud networking costs under control. You can learn more about cloud cost optimization on our site, which might give you some other good ideas.
Staying informed about how these services are priced, and looking for ways to use them more efficiently, will always be a smart move. For more information, you can always see the official
AWS Virtual Private Cloud - VPC

AWS VPC - Create New VPC, Subnets, Internet Gateway
AWS VPC Peering